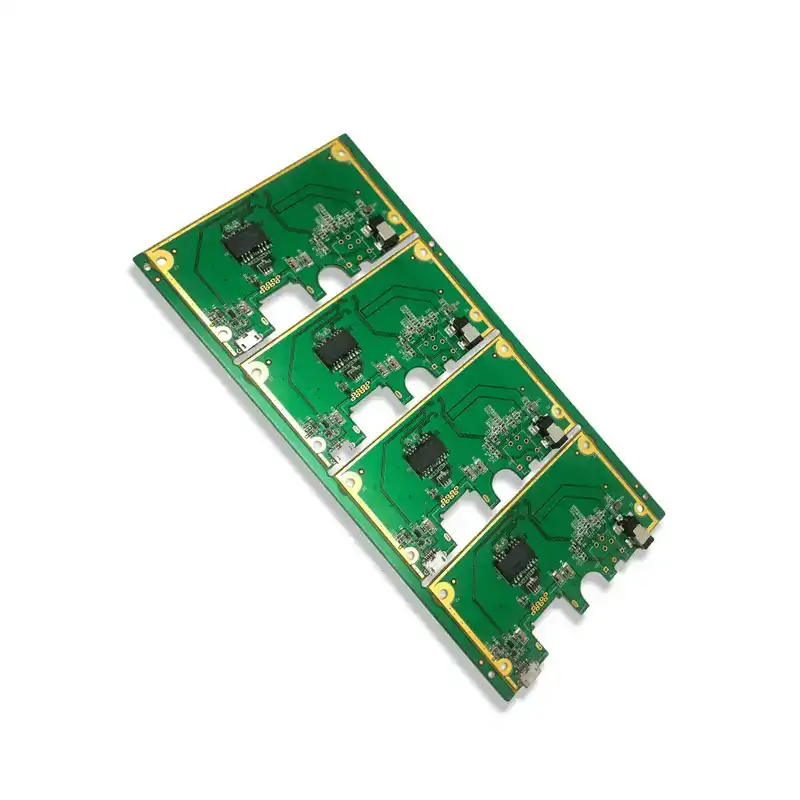
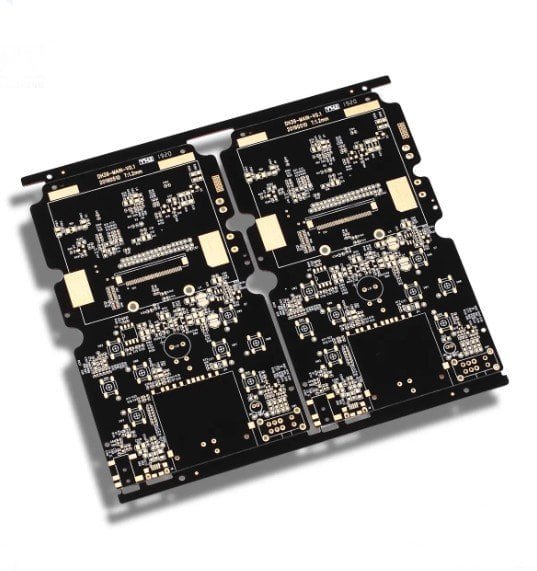
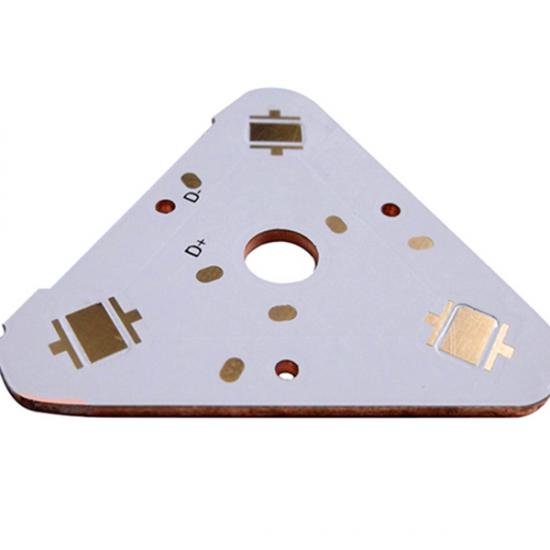
Up to 15 oz Copper PCB Manufacturing Service
Aluminum PCB | Copper PCB | Heavy Copper PCB
QCX Electronic Co., Limited delivers advanced printed circuit board technology and is a leading supplier of Metal-core PCBs. We use cutting-edge technology to provide precision-manufactured PCBs that meet our customers’ rigorous specifications.
Request A Free Quote
What Is Metal PCB?
Metal core printed circuit boards (MCPCB) are a type of printed circuit board that has a metal core layer sandwiched between a layer of dielectric material and a layer of copper trace circuitry. The metal core in MCPCB acts as a heat sink, providing a highly efficient pathway for heat dissipation, which makes them ideal for high-power and high-temperature applications.
The Advantages of Metal PCB
In comparison to traditional FR4 PCB, Metal PCB has a higher thermal conductivity and mechanical stability.
MCPCBs,utilizing a metal substrate such as aluminum or copper, offer excellent thermal conductivity.This allows MCPCBs to have effective heat dissipation in high-power and high-temperature applications,reducing the operating temperature of circuit components and enhancing system reliability and lifespan.
MCPCB is the ideal for applications such as automotive electronics, power supplies, and high-power LED lighting.
MCPCB is available in various types based on the type of metalcore used. Aluminum MCPCB is widely used due to its low cost, lightweight, and good thermal conductivity. Copper MCPCB offers higher thermal conductivity compared to aluminum, but is more expensive and heavier. Other types of metal cores used in MCPCB include steel, nickel, and tungsten.
Fabrication Of Metal PCB (MCPCB)
The fabrication process of MCPCB is similar to that of traditional PCB, but with some additional steps due to the metal core. The following are the steps involved in the fabrication :
Material selection
The first step is to select the appropriate materials based on the specific application requirements. The selection of the metal core, insulation layer, and copper foil will depend on the required thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and mechanical properties.

Photoresist application
A layer of photoresist is applied to the copper layers, which are then exposed to UV light through a photomask to create the desired copper trace pattern.
Solder mask application
A layer of solder mask is applied to both sides of the MCPCB, leaving openings for component placement and soldering.

Drilling
The metal core is drilled with holes for component placement and routing. The drilling is typically done using computer-controlled drilling machines to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Etching
The copper layers are etched away in areas not covered by the photoresist, leaving behind the desired copper trace pattern.

Surface finish application
A final layer of surface finish, typically a layer of metallic or organic material, is applied to the exposed copper traces to protect them from oxidation and other environmental factors.
Copper deposition
A thin layer of copper is deposited on both sides of the metal core using an electroplating process. The thickness of the copper layer will depend on the specific application requirements.
Insulation layer lamination
An insulation layer, typically made of a high-temperature polymer, is laminated onto both sides of the metal core, covering the copper traces.

Testing and inspection
The finished MCPCB is tested and inspected for quality, including electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and mechanical stability.

 EN
EN
 RU
RU


